🚦 1、简述
在高并发场景下,系统如果没有做流量控制,可能会因为请求突增导致 服务过载甚至宕机。常见的限流算法包括:
🔹 固定窗口计数器
🔹 滑动窗口
🔹 令牌桶(Token Bucket)
🔹 漏桶(Leaky Bucket)
样例代码:https://gitee.com/lhdxhl/springboot-example.git
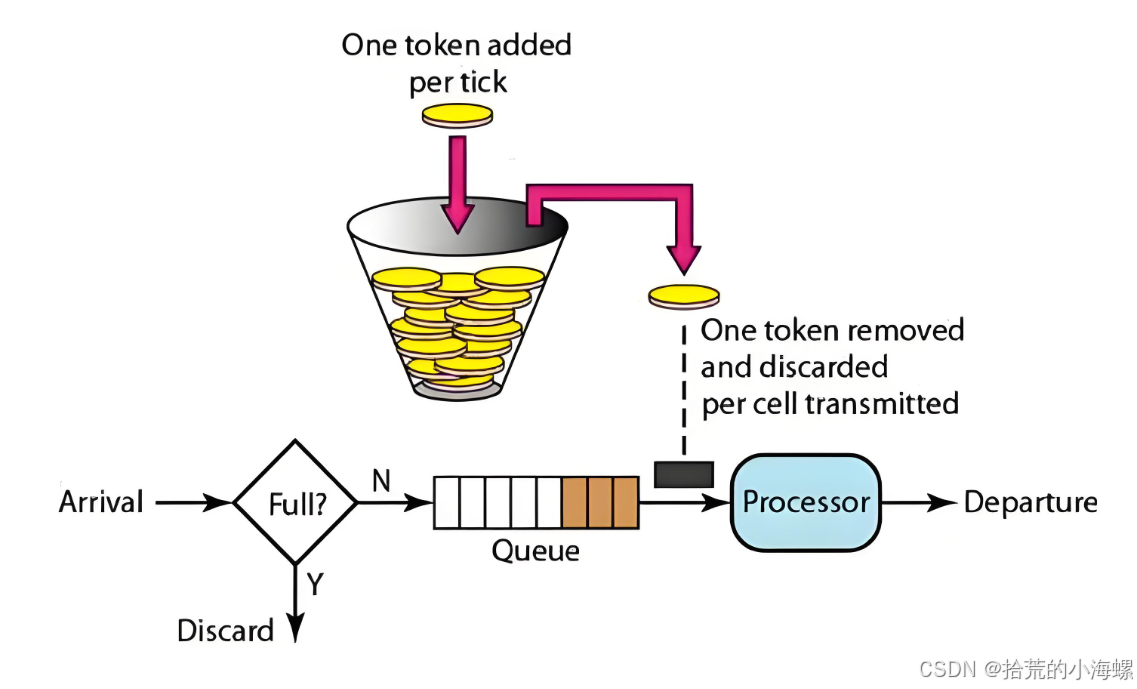
Google 的 Guava 库提供了一个非常优雅的限流工具类:RateLimiter,它基于令牌桶算法实现,能够轻松限制 QPS(每秒请求数)。
2、 原理
🔹 RateLimiter.create(double permitsPerSecond):创建一个限流器,每秒生成 permitsPerSecond 个令牌。
🔹 acquire():从桶里获取一个令牌,如果没有则阻塞等待。
🔹 tryAcquire():尝试获取令牌,如果没有则立即返回 false。
这种方式非常适合 Web 服务的接口限流场景。
3、实践样例
3.1 引入依赖
在 Spring Boot 项目的 pom.xml 中添加:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.google.guava</groupId>
<artifactId>guava</artifactId>
<version>32.1.3-jre</version>
</dependency>
3.2 定义限流配置类
import com.google.common.util.concurrent.RateLimiter;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class RateLimiterConfig {
@Bean
public RateLimiter rateLimiter() {
// 每秒只允许 5 个请求
return RateLimiter.create(5.0);
}
}
3.2 控制器使用限流
import com.google.common.util.concurrent.RateLimiter;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class DemoController {
private final RateLimiter rateLimiter;
public DemoController(RateLimiter rateLimiter) {
this.rateLimiter = rateLimiter;
}
@GetMapping("/api/hello")
public String hello() {
// 尝试获取令牌(非阻塞)
if (!rateLimiter.tryAcquire()) {
return "请求过多,请稍后再试!";
}
return "Hello, 请求成功!";
}
}
3.3 使用 AOP 对接口统一限流(更优雅)
可以通过注解和切面实现 不同接口不同限流规则。
① 自定义注解
import java.lang.annotation.*;
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface RateLimit {
double permitsPerSecond(); // 每秒放行请求数
}
② 切面实现
import com.google.common.util.concurrent.RateLimiter;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
@Aspect
@Component
public class RateLimitAspect {
private final ConcurrentHashMap<String, RateLimiter> limiters = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
@Around("@annotation(rateLimit)")
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint, RateLimit rateLimit) throws Throwable {
String key = joinPoint.getSignature().toShortString();
RateLimiter rateLimiter = limiters.computeIfAbsent(key,
k -> RateLimiter.create(rateLimit.permitsPerSecond()));
if (!rateLimiter.tryAcquire()) {
return "接口被限流,请稍后再试!";
}
return joinPoint.proceed();
}
}
③ 控制器使用注解
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class ApiController {
@RateLimit(permitsPerSecond = 2.0) // 每秒最多 2 次请求
@GetMapping("/api/data")
public String getData() {
return "成功返回数据";
}
}
3.4 测试效果
🔹 启动 Spring Boot 应用;
🔹 快速刷新 /api/data 接口;
🔹 你会发现大部分请求返回 "接口被限流,请稍后再试!"。
这样,我们就利用 Guava + Spring Boot 快速实现了接口限流。
4、总结
🔹 RateLimiter 基于 令牌桶算法,适合做接口级别的限流;
🔹 简单场景下可以直接在 Controller 使用;
🔹 复杂场景推荐通过 注解 + AOP,实现多接口灵活限流;
🔹 如果需要分布式限流,可以结合 Redis、Sentinel 等工具。

